
Condition Monitoring
to Stay Ahead
Table of Contents
ToggleCondition Monitoring
What is Condition Monitoring?
Condition monitoring is the process of determining the equipment fitness, by monitoring critical parameters (eg. temperature, pressure, vibration). Abnormalities observed are indicative of developing problems that can lead to potential failure. Proactive condition monitoring helps in identifying failures at the initial stage, before they develop into major breakdowns, thus avoiding downtime and its consequences. MaintWiz’s Asset Management platform integrates with Condition Monitoring to provide real-time asset data and enable predictive maintenance strategies.
Condition monitoring is effectively used in equipment with moving or rotating parts (eg. pumps, motors), whereas techniques like non-destructive testing are used in stationary equipment (eg. boilers, storage tanks). Condition monitoring techniques can also be applied to the production output to determine flaws in the manufacturing process. Ultrasound testing can detect variations in material thickness or flaws beneath the surface.
Condition monitoring can be discrete or done over specific time intervals or monitored continuously over time. It can give near real-time status, operating condition or position of the underlying equipment and often can give warning symptoms of imminent breakdown. By integrating Predictive Maintenance with Condition Monitoring, you can anticipate equipment failures and improve overall asset performance.
Values of the parameter captured can be compared against equipment standards or plotted as a performance trend over time or compared to the performance of a similar class of equipment. Deviations detected trigger further actions including alerts and notifications and generation of preventive maintenance work orders.
Improving Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) with Condition Monitoring allows you to track equipment performance and maximize uptime.
Benefits of Condition Monitoring
1.Monitoring: Monitoring and evaluation are essential to maintain the equipment condition under control and to determine the nature of intervention to avoid failures. Prevent breakdowns by combining Condition Monitoring with Breakdown Maintenance, ensuring minimal downtime and higher equipment reliability.
2.Diagnostics: Comprehensive information on equipment condition and behavior to troubleshoot and analyze the root cause quickly and efficiently for prompt resolution.
3.Prognostics: First Symptom alerts generation, much before the occurrence of catastrophic failure to define preventive maintenance programs.
4.Reliability: Increase reliability of the system through multi-dimensional analysis and probabilistic models.
5.Better Return on Assets: Condition monitoring prevents catastrophic failures, thereby improving equipment uptime and operations. Preventive maintenance programs ensure increased asset life and better utilization.
Condition Monitoring Techniques
Condition monitoring finds many applications in managing industrial assets. Frequent condition monitoring techniques include:
- Acoustic emission testing
- Alignment systems
Electric signature analysis - Erosion / Corrosion analysis
- Hydraulic analysis
- Infrared thermography
- Lubricant analysis / Debris analysis
- Model-based voltage and current systems (MBVI systems)
- Noise and vibration analysis
- Optical inspection
- Orifice restriction monitoring
- Performance monitoring
- Pressure / Liquid flow rate
- Stress / Strain Analysis
- Thermometry
- Torque / Speed Measurement and analysis
- Tribology
- Ultrasonics
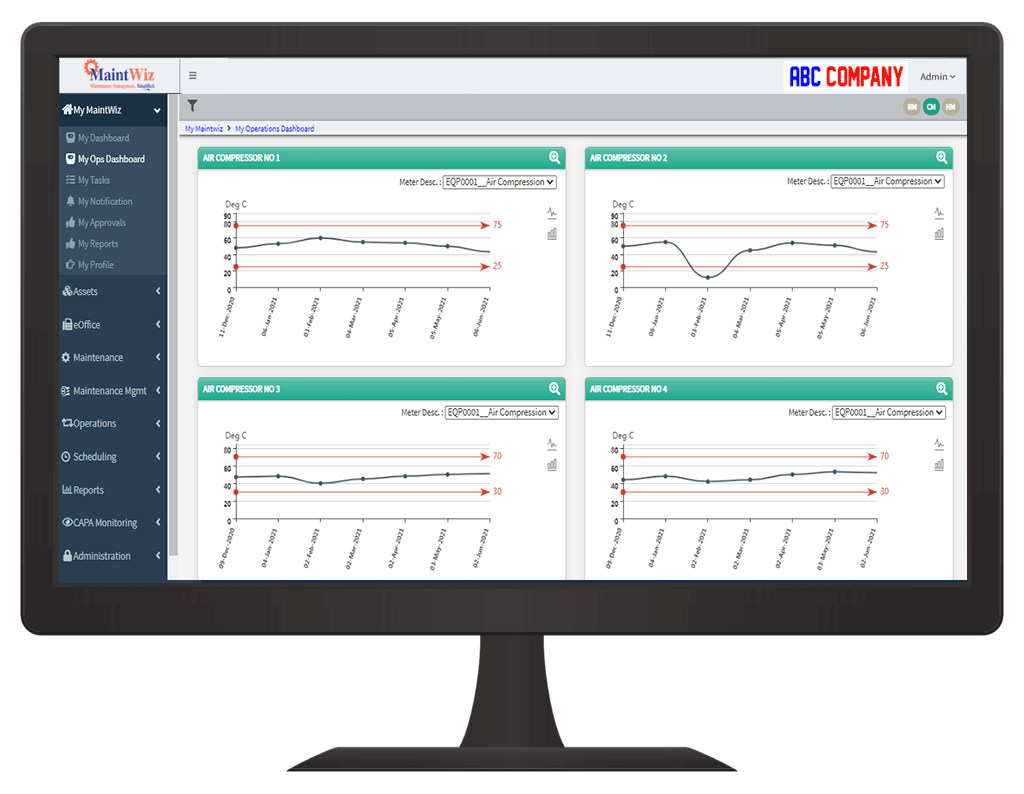
How to do Condition Monitoring?
Condition monitoring implementation should flow from enterprise maintenance strategy. Condition monitoring system for an equipment is determined based on multiple factors including equipment criticality, operating condition, risk levels, the impact of a breach to people, assets and environment, etc. Based on the goals, a set of parameters that mirror the equipment condition and the frequency of monitoring are determined. Often there can be multiple independent sets of such parameters to monitor different aspects of condition and behavior.
Implementing condition monitoring requires specialized knowledge on five key aspects:
Determining the objectives and translating them into the set of parameters that needs to be monitored and the frequency of data monitoring (discrete, periodic or continuous).
Interpreting the parameter or a set of related parameters to ascertain the significance.
Defining the limits of normal operation and abnormal operations and setting up first symptom alerts.
Determining what countermeasures should be taken on a breach.
Building a robust system to capture the condition monitoring data and translating it to desired outcomes.
Analysing the condition monitoring signals and interpreting inferences requires deep domain expertise and specialized skills and training. For the same equipment, condition monitoring of lubricant analysis and vibration acoustics require diverse skills and knowledge.
Role of CMMS in Condition Monitoring
Manual interventions required for condition monitoring restricted its frequency and application in the past and were often restricted to tracking very few critical parameters. The proliferation of built-in processors and control systems in modern equipment makes available enormous data today. The data explosion has resulted in a paradigm shift in the usage of data, from complete consumption to exception handling. Volume, variety, and velocity of data has made manual analysis inadequate and enforced automated processing.
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) hosts all the condition monitoring information that gets captured by different independent systems. Modern CMMS comes with a powerful rules engine that can validate these parameters against set rules. Advanced analytical tools can provide statistical data analysis, what-if scenarios, and visual representations. System modeling of the underlying equipment, multi-factor analysis and simulation can portray equipment behavior under adverse operating conditions to improve equipment reliability and execute predictive maintenance.
Why is MaintWiz the best solution for you?
MaintWiz is a new age industry 4.0 CMMS platform that helps you to capture all the information from devices, sensors, SCADA, Internet of Things and other automated sources onto a common platform and enables triggers based on business rules. It’s a full-service platform enabling the recording, hosting, analyzing, modeling of data and predicting the equipment behavior.
MaintWiz is offered as a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solution, with mobile enablement to facilitate data capture at the point of work by the operational staff. MaintWiz is a Simple, Easy-to-use, Integrated, Cost-effective and Scalable solution. Primary benefits of the solution include:
1.Capture diverse information from automated sources through web services.
2.Hybrid meters for combinatorial analysis of related parameters.
3.Ability to set up comprehensive business rules for data validation.
4.Alerts and notifications to broadcast first symptoms. Triggers for generating preset downstream actions.
5.Powerful analytics to support data processing, modeling and scenario building.
6.Integration with enterprise systems like ERP, SCADA, Data Warehouse and other in-house systems.
7.Build predictive maintenance capabilities to support smart manufacturing.
Interested in implementing Condition Monitoring for your assets? Request a demo to explore how MaintWiz can help.
Request a one-one demo with our solution engineering team.

Request a one-one demo with our solution engineering team.




