Optimize Maintenance Workflows with MaintWiz CMMS Work Order Management
MaintWiz CMMS revolutionizes work order management, ensuring seamless task execution from creation to completion. Our AI-powered platform integrates automated scheduling, real-time updates, and SAP integration, empowering your maintenance teams to achieve unprecedented efficiency and performance.
Work Order Management
Dive into Detailed Product Information and address your common queries.
Speak to a Specialist
Get personalised advice from our experts
Streamlined Work Order Creation & Request Management with AI driven Automation
Harness the power of artificial intelligence to transform your maintenance operations. MaintWiz CMMS leverages cutting-edge AI algorithms to optimize work order creation, prioritization, and resource allocation, ensuring maximum efficiency and minimal downtime.
Comprehensive Work Order Creation and Request Management
From breakdowns to preventive maintenance and shutdown tasks, MaintWiz CMMS allows you to manage every type of work order efficiently. Simplify your workflow with an all-in-one solution that captures all maintenance requests in one place.
Multi-Channel Maintenance Request Optimization for Rapid Response
MaintWiz CMMS centralizes work order creation through web, mobile work order app, and automated triggers. Our intuitive interface auto-populates known fields, enabling quick submissions for all maintenance types – from breakdowns to preventive tasks.
Intelligent Automated Work Order Generation for Proactive Maintenance
Leverage our system’s automated work order creation capabilities to stay ahead of equipment issues. MaintWiz CMMS software integrates with preventive maintenance schedules or real-time IoT sensor data, ensuring timely interventions and reducing unexpected downtime.
Streamline Approval Workflows for Optimal Resource Allocation
Implement customizable approval processes that align with your organizational structure. MaintWiz CMMS software’s workflow management ensures proper authorization, prioritization, and resource allocation for all maintenance activities.
Comprehensive Work Order History for Informed Decision-Making
Gain instant visibility into past maintenance activities with our centralized work order history database. This historical context empowers technicians and managers to make data-driven decisions, improving maintenance strategies over time.
Enhance User Experience with Intuitive Request Forms
Empower production users with simple, user-friendly work order request forms. MaintWiz CMMS software’s interface design reduces friction in the reporting process, ensuring critical maintenance needs are communicated promptly and accurately.
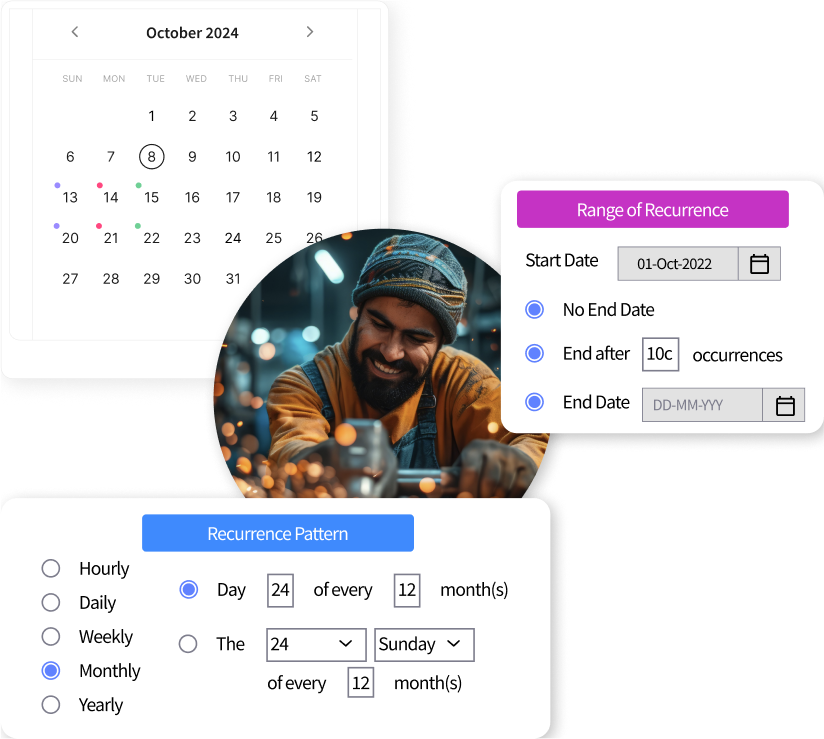
Optimize Planning with an All-Encompassing Maintenance Calendar
Visualize all scheduled maintenance activities in one comprehensive calendar. MaintWiz integrates work orders with preventive maintenance schedules, enabling better resource planning and minimizing conflicts.
Top Companies in India & Abroad Trust MaintWiz CMMS
















Comprehensive Work Order Execution & Real Time Tracking
Experience the future of maintenance management with MaintWiz's smart work order execution and tracking. Our intelligent system optimizes technician assignments, provides real-time insights, and continuously learns from your maintenance data to improve efficiency and reduce downtime.

Maximize Efficiency with Smart Work Order Assignment and Scheduling
MaintWiz CMMS helps to assign matches tasks to suitable technicians, optimizing workforce utilization and reducing response times for critical maintenance needs.
Ensure Consistency with Detailed Checklists and Step-by-Step Instructions
Standardize maintenance procedures using customizable checklists and task instructions. MaintWiz empowers technicians with clear guidelines, ensuring consistent quality of work and compliance with OEM recommendations. Minimizes rework and improves maintenance effectiveness.
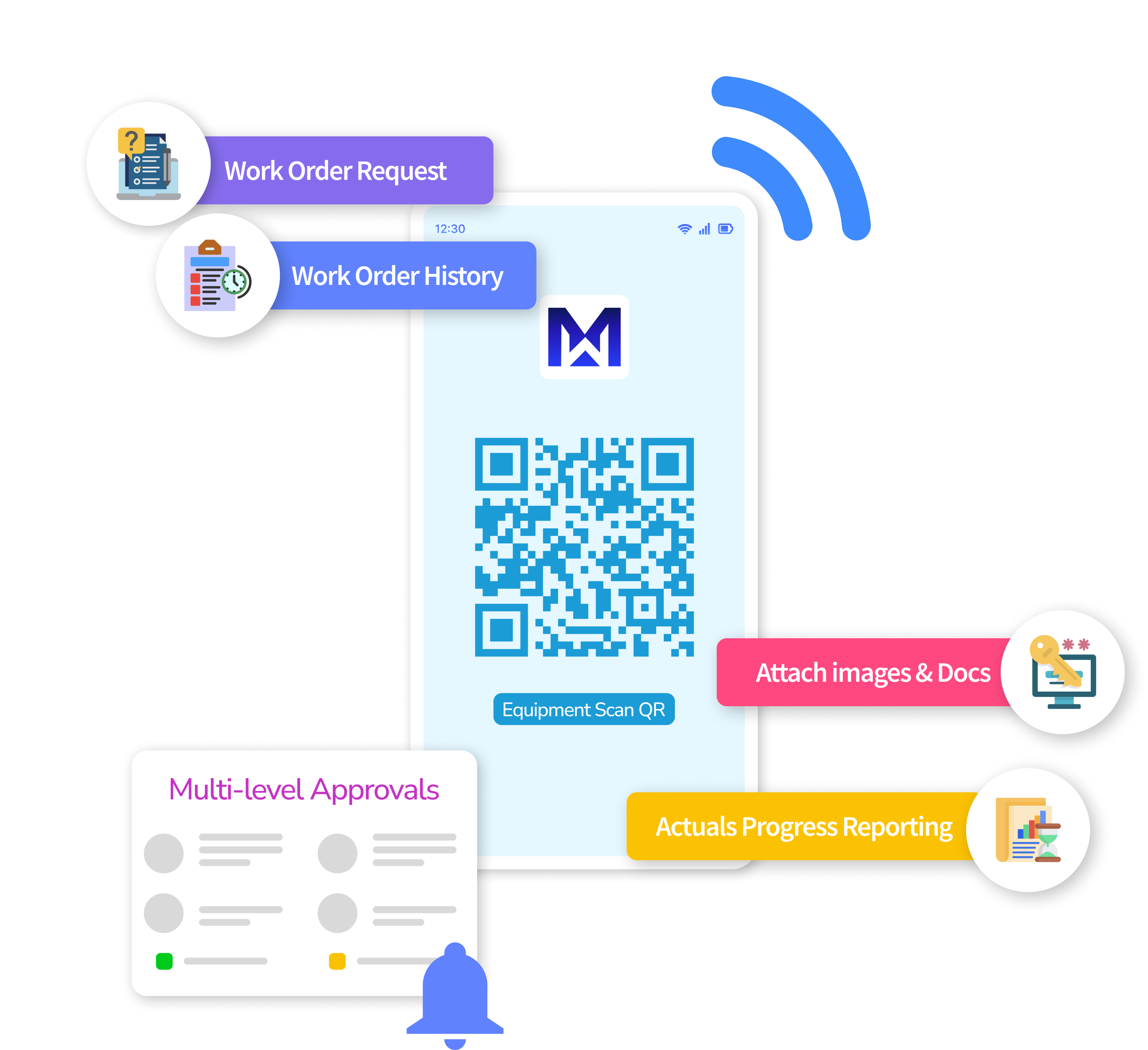
IoT Enabled Mobile Technology for Real-Time Asset Management
Equip your team with MaintWiz’s mobile work order app for on-the-go access. Technicians can update work order status, scan QR codes for quick asset identification, and track part usage in real-time, enhancing overall maintenance efficiency.
Monitor Progress with Live Status Updates to Prevent Delays
Stay informed with real-time work order status updates. MaintWiz’s live tracking feature allows managers to identify bottlenecks, allocate resources dynamically, and ensure timely completion of maintenance tasks.
Intelligent Labor and Parts Usage Tracking for Cost Optimization
Capture time and material costs directly within work orders. MaintWiz’s integrated tracking system provides precise data for maintenance cost analysis, helping optimize resource allocation and budgeting.
Seamlessly Integrate Digital Safety Permits with Work Orders
Ensure workplace safety with MaintWiz’s integrated safety permit system. Create, approve, and close out safety permits directly within work orders, maintaining compliance and protecting your workforce.
Our Benefits
Work Order Closure & Root Cause Analysis
Transform your maintenance insights with MaintWiz's AI-driven work order closure and analysis tools. Our advanced algorithms process completion data to provide predictive maintenance recommendations, optimize resource allocation, and drive continuous improvement in your maintenance operations.
Simplify Work Order Closure with Comprehensive Feedback Analysis
Streamline the work order close-out process with MaintWiz CMMS software’s user-friendly interface. Technicians can easily input completion notes and feedback, ensuring valuable insights are captured for future maintenance improvements.
Implement Root Cause Analysis for Continuous Improvement
Utilize MaintWiz’s built-in root cause analysis tools to identify recurring issues. Our system facilitates the development and tracking of corrective and preventive actions, driving continuous improvement in maintenance practices.
AI-Powered Predictive Analytics for Data-Driven Decision Making
Harness the power of MaintWiz’s comprehensive analytics and reporting capabilities. Our system provides detailed insights into work order trends, enabling managers to make informed decisions and optimize maintenance strategies.
Automated Compliance Reporting with Efficient Audit Preparation
Stay audit-ready with MaintWiz CMMS software’s compliance reporting features. Our system generates detailed reports based on completed work orders, simplifying the process of demonstrating regulatory compliance.
KPI Tracking for Maintenance Excellence
Monitor crucial maintenance metrics like MTTR and MTBF with MaintWiz CMMS’ advanced analytics. Our KPI tracking tools provide a clear picture of maintenance performance, helping you identify areas for improvement.
Build Comprehensive Asset Histories for Informed Maintenance Planning
Create detailed asset lifecycle records by linking completed work orders to equipment histories. MaintWiz CMMS software provides comprehensive asset and work order history, for future maintenance decisions and replacement planning.
Voices of Our Valued Clients
Efficient Enterprise System Integration for Holistic Management
Unlock the full potential of your maintenance operations with MaintWiz's enterprise system integration. Our intelligent platform seamlessly connects with your existing software ecosystem, providing unparalleled insights, streamlined workflows, and predictive maintenance capabilities across your entire organization.
Seamless SAP / ERP Integration for Unified Data Management
With MaintWiz CMMS’ powerful integration capabilities, unify your maintenance and financial data with SAP / other ERP. This seamless connection ensures accurate cost control, streamlined budgeting, and comprehensive asset lifecycle management.
Intelligent Inventory Optimization with Predictive Procurement
Enhance parts availability by connecting work orders directly to procurement processes. MaintWiz CMMS integrated approach ensures timely ordering of necessary components, reducing maintenance delays and inventory costs.
Intelligent Project Management for Large-Scale Maintenance Initiatives
Maximize efficiency of large maintenance projects by linking work orders to broader maintenance initiatives. MaintWiz CMMS’ project management features allow for coordinated execution of complex maintenance tasks and capital projects.
AI-Powered IoT Integration for Advanced Predictive Maintenance
Harness the power of IoT sensors to trigger timely maintenance interventions. MaintWiz’s IoT integration capabilities enable real-time condition-based maintenance, reducing unexpected failures and optimizing asset performance.
Efficient Vendor Management for Outsourced Maintenance
Streamline collaboration with external service providers through MaintWiz’s vendor management system. Our platform facilitates seamless communication, work order assignment, and performance tracking for outsourced maintenance tasks.
Ensure Regulatory Compliance with Integrated Audit Management
Simplify compliance processes with MaintWiz’s built-in audit management tools. Our system helps track regulatory requirements, schedule necessary inspections, and maintain comprehensive records for seamless audits.
Optimize Workflows and Boost Productivity with Smart Work Order Solutions
Empower your maintenance team with MaintWiz’s intelligent work order management tools. Assign tasks, track progress, and automate workflows effortlessly. By streamlining scheduling and execution, you’ll enhance productivity, reduce downtime, and ensure that every maintenance task is completed on time and within budget.
Breakdown Maintenance Tracking
Track and resolve unplanned breakdowns in real time for quick recovery.
Digital Logbook for Maintenance
Maintain a centralized digital log of all maintenance activities for easy tracking.
Preventive Maintenance Scheduling
Efficiently plan and schedule preventive maintenance tasks with MaintWiz.
IoT-Enabled Maintenance
Utilize IoT data to automate work order creation based on asset conditions.
Condition Monitoring Solutions
Track real-time asset conditions and trigger automated work orders for maintenance.
Predictive Maintenance Tools
Leverage data-driven insights to predict failures and minimize downtime.
Reliability Centered Maintenance
Prevent critical failures and ensure reliability with corrective actions.
Safety Permit Integration
Integrate safety permit approvals into work orders for compliance and safety.
Request a one-one demo with our solution engineering team.
Request a one-one demo with our solution engineering team.






MaintWiz streamlined our work order process, drastically reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency